Types and differences…
While prostate-related abnormalities or diseases can be of many kinds and forms, the most common and important prostate disorders include the following:
- Prostatitis (Acute & chronic)
- BPH
- Prostatic carcinoma
Let’s learn about each of these, one by one:
What is prostatitis?
For men under 50, the most common prostate problem is prostatitis. As a common general knowledge, you should always remember that whenever any term or word ends in the suffix “…itis”, it almost always means inflammation of some particular part, gland or organ of your body. Gingivitis, for example, refers to the inflammation of gums. Similarly, dermatitis refers to the inflammation of your skin. The same goes for your prostate as well. So, prostatitis is simply the “inflammation of prostate”.
What are the types of prostatitis?
Generally speaking and on the basis of its severity and duration, prostatitis can be divided into two main types or forms:
- Acute prostatitis
- Chronic prostatitis
What is the difference between acute and chronic prostatitis?
Acute prostatitis
Acute prostatitis comes all of a sudden and is characterized by severe symptoms such as painful urination; inability to empty the bladder while urinating and sharp in and around lower abdomen and fever and chills with some cases.
Chronic prostatitis
A prostatitis that keeps coming back again and again is called chronic prostatitis. It develops gradually, persists for long-term and can be caused due to bacteria. However, in many cases, bacteria are not involved. This subtype of chronic prostatitis is known as “non-bacterial prostatitis”.
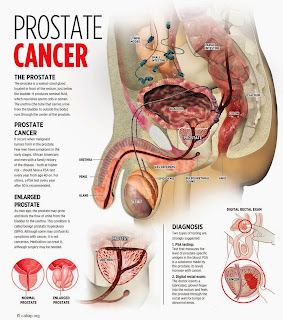
What is BPH?
In its simplest definition, the term “Benign Prostate Hyperplasia” (BPH) refers to the noncancerous enlargement of prostate gland.
As men get older, their prostates may get bigger and restrict the flow of urine and this is known as BPH.
To better understand BPH, let’s have quick review of the following related terms:
Benign: This refers to anything that does not have a potential to “spread”. In other words, a tumor that is “not cancerous” is known as benign.
Hyperplasia: This refers to an increase number of muscle fibers which leads to an “increased” (enlarged) size of that organ or gland.
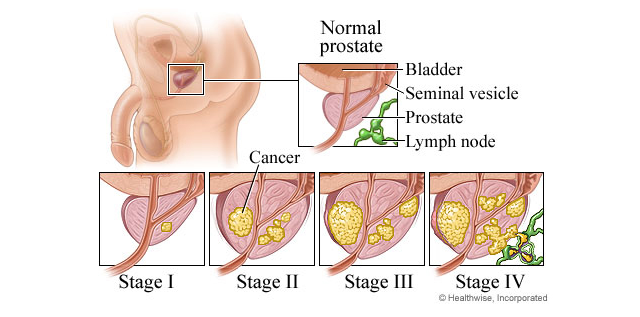
What is prostate cancer?
Medically known as prostatic carcinoma, a cancer of the prostate gland is known as prostate cancer. As mentioned in the previous chapter, prostate cancer is the second most common cancer found in men especially in US (after skin cancer). However, it is mainly a disease of the old age.
In its early stages, prostate cancer may remain dormant or “silent” without causing any signs or symptoms. The first noticeable symptoms are usually similar to those found in BPH such as frequency, hesitancy, urgency and incontinence. More severe stages of cancer may present as:
- Blood in the urine or semen (Medically known as hematuria)
- Impotence (Medically known as erectile dysfunction)
- Pain in back, hips or pelvis